The Application and Practice of Flowmeters in Chemical Production

In the closed-loop automatic control system of chemical production, pressure, liquid level, temperature and flow rate are collectively known as the four core process parameters. Among them, the flow rate parameter directly determines the accuracy of reactant ratio, energy consumption efficiency and product quality stability. As a key device for monitoring flow parameters, the flowmeter is like a "pulse monitor" in a chemical production line. Its measurement accuracy and operational stability directly affect production safety, environmental compliance and economic benefits. This article will start from the demands of the chemical industry and systematically analyze the core value, mainstream types and key points of full-process application of flowmeters.
The core requirements for flowmeters in chemical engineering scenarios
The diversity of media and the complexity of working conditions in chemical production impose strict requirements on flowmeters, which can be specifically summarized into three core demands:
1.1 Accuracy Adaptability: The accuracy requirements vary significantly across different scenarios. In metrology-level scenarios such as trade settlement and carbon emission accounting, an accuracy of ±0.2%FS to ±0.5%FS is required, while in control-level scenarios like reactor feed control, a repeatability of ±0.1%FS and a response speed of less than 500ms are emphasized. For instance, in the production of synthetic ammonia, even a slight deviation in the flow rate of raw gas can lead to a decrease in the conversion rate, and it is necessary for the flowmeter to maintain long-term high-precision and stable operation.
1.2 Working Condition Tolerance: Chemical media often have corrosive and high-viscosity properties. The working conditions mostly involve high temperature and high pressure (for example, the temperature of heat transfer oil can reach 350℃, and the pressure of reaction vessels exceeds 10MPa), and in some scenarios, there is a risk of flammability and explosion. Therefore, the flowmeter is required to have the corresponding explosion-proof grade (such as intrinsically safe type ExiaIIC T6 or flameproof type ExdIIC T6) and weather resistance of the material.
1.3 System Compatibility: It must support industrial communication protocols such as HART and Modbus, and be seamlessly integrated into DCS/SCADA control systems to achieve real-time upload of flow data, remote monitoring, and interlocking control with actuators such as valves, providing data support for production optimization.
2. Key Points for the full-process application of flowmeters
The precise operation of flowmeters relies on the full-process control of "selection - installation - maintenance - calibration". Any oversight in any link may lead to measurement deviations and even cause production accidents.
2.1 Scientific Selection: Matching the working conditions is the prerequisite
Selection requires the establishment of an evaluation system: First, clearly define key parameters such as the medium type (liquid/gas/slurry), conductivity, and viscosity; Secondly, confirm the temperature, pressure range and explosion-proof requirements; Finally, select the accuracy grade in combination with the measurement target (metrological grade/control grade/monitoring grade). For instance, in the demineralization system of a certain power company's boiler water, the initial selection of vortex flowmeters led to measurement deviations due to insufficient straight pipe sections. After replacing them with Coriolis flowmeters without the requirement for straight pipe sections, the accuracy of chemical dilution was significantly improved, and the chemical cost was reduced by 30%.
2.2 Maintenance Calibration: The guarantee for stable operation
Daily maintenance should be carried out in a differentiated manner based on the type of flowmeter: for vortex flowmeters, clean the vortex generator every three months; for electromagnetic flowmeters, clean the surface of the lining every six months; and for ultrasonic flowmeters, check the status of the transducer annually. The calibration cycle should be matched with the application scenarios. For metrology-level scenarios, calibration should be carried out once every six months, while for control-level scenarios, it should be done once a year. The calibration adopts the real-flow calibration method, covering the three key nodes of 10%, 50%, and 90% of the measurement range, to ensure that the linearity error is ≤0.5%FS.
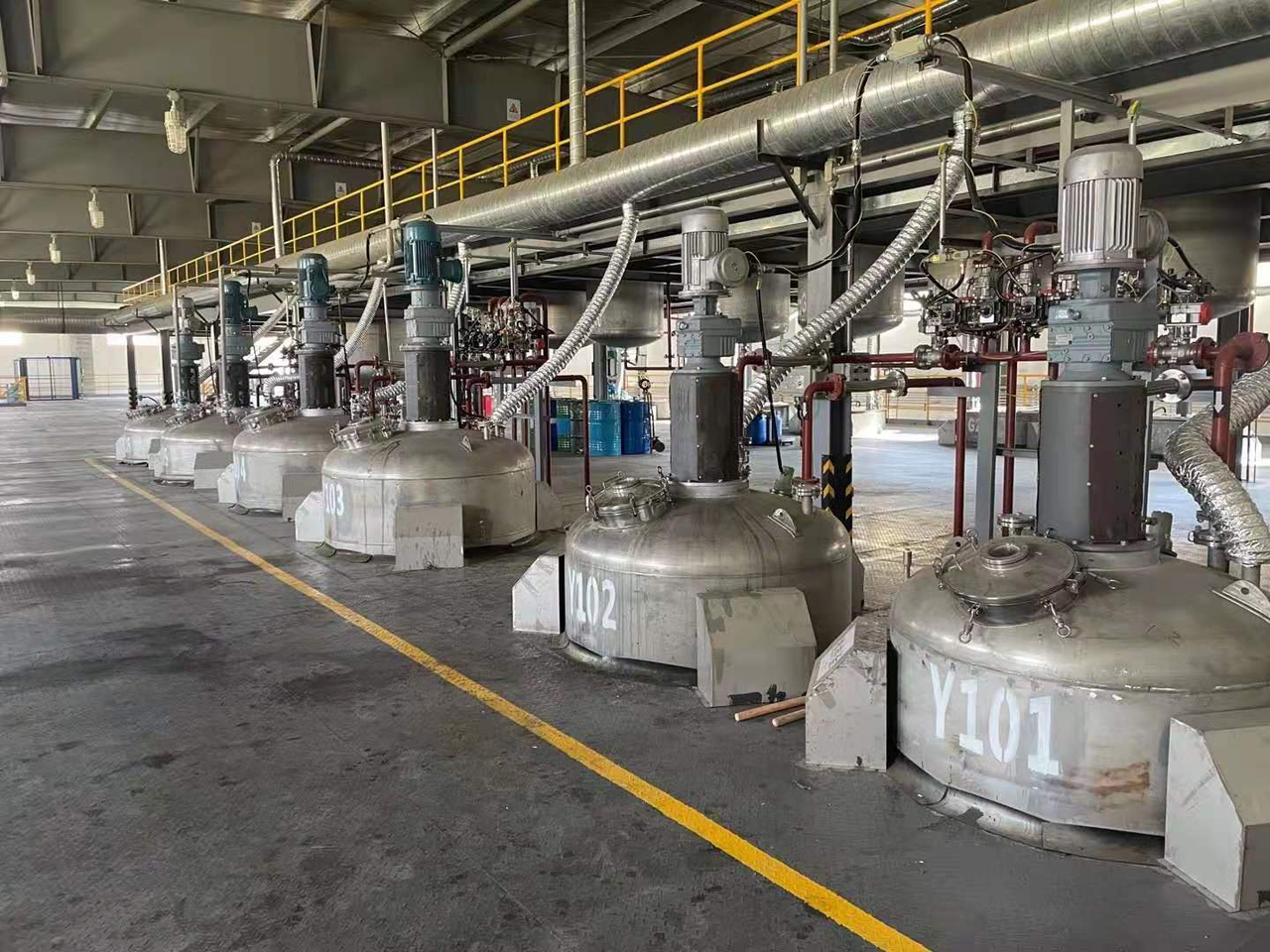
3. Practical Application cases: From Problem to Solution
A certain ammonia synthesis production enterprise once faced the problem of unstable ratio of raw gas (hydrogen and nitrogen), which led to an ammonia conversion rate of only 82% and relatively high energy consumption. After investigation, it was found that the originally used differential pressure flowmeter had a measurement error of ±2.5% due to the compressibility of the gas, which could not meet the precise ratio requirement of 1:3.
Solution: Replace with a vortex flowmeter. This type has optimized the temperature and pressure compensation algorithm for gas media, improving the measurement accuracy to ±0.8%. Moreover, it adopts a dual vortex structure and damping alloy materials, effectively resisting the interference of pipeline vibration. At the same time, the flow data is connected to the DCS system through the Modbus protocol to achieve interlocking control with the feed valve. When the flow deviation exceeds ±0.5%, the valve opening is automatically adjusted. After the transformation, the accuracy of the raw gas ratio remained stable within ±0.3%, the ammonia conversion rate increased to 89%, and the annual energy consumption cost was reduced by approximately 1.2 million yuan.
4. Conclusion: The intelligent upgrade direction of flowmeters
With the transformation of the chemical industry towards "intelligent manufacturing", flowmeters are upgrading from single measurement devices to integrated terminals of "perception - analysis - diagnosis". In the future, intelligent flowmeters with wireless communication, predictive maintenance (predicting faults through vibration and temperature data), and edge computing capabilities will become mainstream. Combined with industrial Internet platforms, they will achieve full life cycle management of flow data, providing more solid support for precise control and energy conservation and consumption reduction in chemical production.